Phobia, or panic, is a disorder characterized by experiencing intense fear toward specific situations, places, or things in an illogical manner. Phobia patients suffer from uncontrollable panic responses to these specific elements. It is not just fleeting fear but is considered a disorder that requires treatment.
Phobia Definition:
Medically, phobia disorder is defined as an illogical reaction accompanied by a high level of fear, tension, or panic. This occurs when an individual faces a specific situation or sees a specific thing or is present in a specific place. Phobia disorder is distinguished from general anxiety disorders by a constant feeling of fear. Phobia patients have difficulty controlling their reactions. Phobia patients are fully aware of their condition and fully aware that their reaction and level of fear are exaggerated. But they are unable to overcome these excessive physical reactions.
Types of Phobia:

Phobia, or panic, appears in various forms. Although new types of phobia are always being discovered, some of the most common cases include:
1. Claustrophobia: Individuals suffering from this type of phobia experience fear and panic when in crowded or difficult-to-escape places, leading them to avoid social situations and prefer isolation.
2. Social Phobia: Patients with this disorder have difficulty interacting with others, even responding to phone calls or entering public places can cause severe anxiety.
3. Glossophobia: Characterized by severe fear of speaking in front of others, accompanied by physical symptoms when thinking about facing people.
4. Acrophobia: Intense fear of climbing mountains or high floors, leading to severe dizziness when in high places.
5. Agoraphobia: Intense fear of being in enclosed or tight places, such as taking an elevator or a car.
6. Aviophobia: Here the fear of flying, where patients expect to crash and crash.
7. Dentophobia: Patients here suffer from a severe fear of visiting the dentist.
8. Homophobia: Here comes the fear of blood, with a high level of fear that can lead to loss of consciousness upon seeing blood.
9. Arachnophobia: Some enter into bouts of horror and extreme fear upon seeing spiders.
10. Reptile Phobia.
11. Nyctophobia.
Types of Rare Phobia:
High-pitched sound phobia.
Dirt phobia.
Youth phobia.
Mirror phobia.
Meat phobia.
Hair phobia.
Stranger phobia.
Outdoor phobia.
Phobia of holes.
Balloon phobia.
Vomiting phobia.
Long word phobia.
People Most Vulnerable to Phobia
Individuals with a family history of mental disorders are more likely to develop phobia. Studies also show that women may be more susceptible to developing phobia, especially animal phobia. On the other hand, individuals with low social status often suffer from social phobia, while a large proportion of men show dental phobia.
Causes of Phobia:
There are various causes and factors that may increase the likelihood of developing phobia, including:
1. Genetic and Environmental Factors: Having a family history of mental disorders and phobia is a factor that may increase the likelihood of developing this disorder. The environment in which the individual lives may also play a significant role in the formation of this type of disorder.
2. Suffering from Depression and Anxiety: Some suggest that phobia may be associated with depression and anxiety. Negative experiences or previous incidents may exacerbate the condition and lead to the appearance of phobia symptoms.
These factors demonstrate how the formation of phobia can be the result of a complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors, in addition to psychological factors such as depression and anxiety.
Symptoms of Phobia:
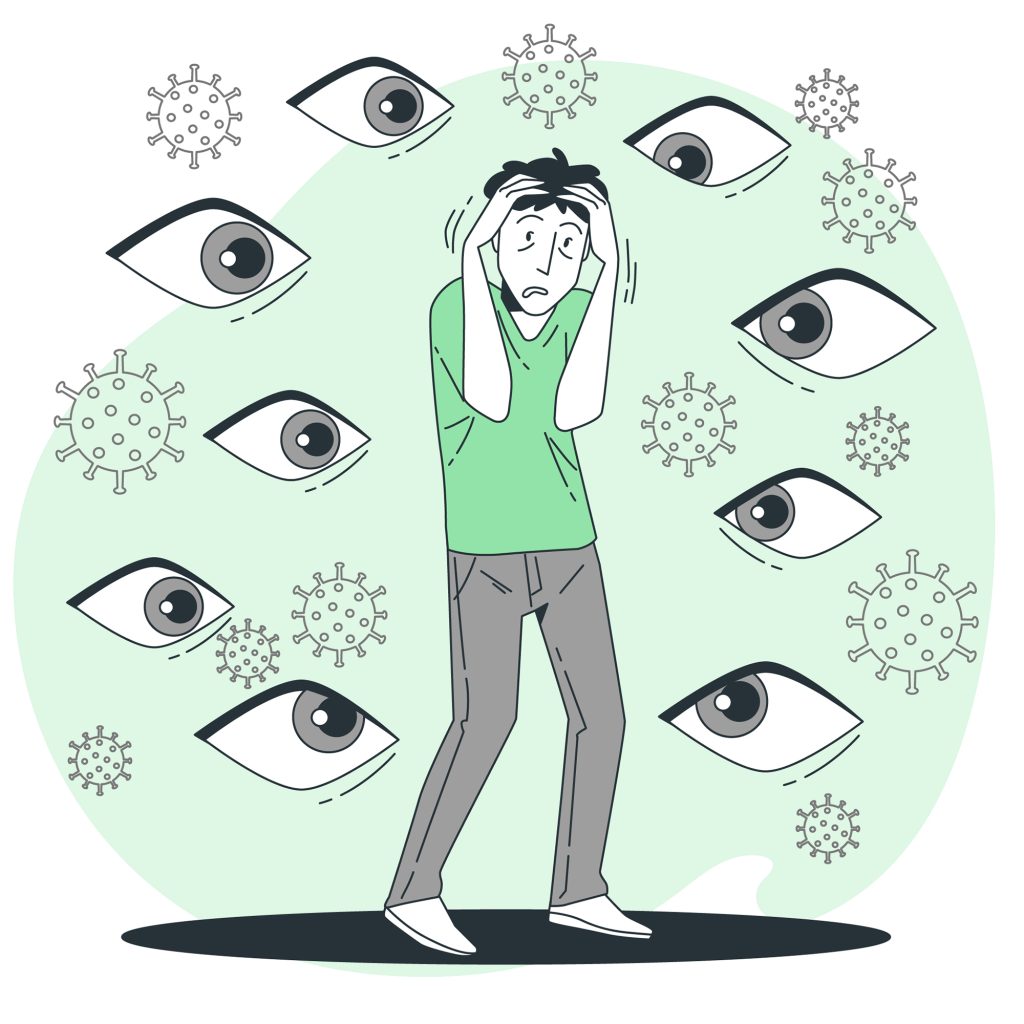

A sharp increase in heart rate and pulse rate.
A sense of shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
Stomach disorders, such as nausea.
Feeling dizzy and nauseous.
Fast speech accompanied by difficulty in speech in some cases.
Chest pain.
Body tremors.
High blood pressure.
Increased sweating.
Absolute belief in the existence of danger that could lead to death.
These symptoms represent strong physical and psychological reactions that individuals with phobia may experience when faced with situations or things that trigger their fear.
Phobia Treatment Methods:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy is considered one of the most effective methods for dealing with phobia cases. This therapy involves gradually exposing the patient to fear-provoking situations, monitoring reactions, and developing anxiety control strategies.
2. Medication: In some cases, antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications are used to reduce the physical and psychological symptoms of phobia. It is important to consult a doctor before starting any drug therapy.
Prevention of Phobia:
Prevention of phobia can be achieved through increasing general awareness about this disorder and promoting community understanding of how to deal with patients. Talking about psychological and emotional challenges is also encouraged to reduce depression and anxiety.
Dealing with Phobia Patients:
Patients should be approached and provided with psychological support. It is advisable to talk to them about the causes of anxiety and avoid fear-provoking situations. Visiting psychological treatment centers and speaking to specialists is encouraged.
How Does a Phobia Patient Comfort Himself?
It is best for the individual with phobia to identify the source of anxiety and discuss it with trusted people. Avoiding fear-provoking situations is encouraged, and adopting a positive thinking style and repeating the affirmation that difficult situations will be overcome.
In conclusion, comprehensive treatment for phobia by combining cognitive behavioral therapy and drug therapy is highly effective. Prevention and effective dealing with phobia patients contribute to improving their quality of life and reducing negative psychological impact.

No comment